
Content Menu
● Introduction to Food Dehydrators
>> Importance of Cooling in Dehydration
● Technologies for Cooling Food Dehydrators
>> 1. Heat Pump Technology
>> 2. Dehumidification Heat Pumps
>> 3. Low-Temperature Drying Machines
● Additional Strategies for Cooling
>> 1. Proper Placement and Ventilation
>> 2. Avoid Heated Areas
>> 3. Regular Maintenance
>> 4. Insulation and Thermal Management
>> 5. Smart Sensors and Automation
● Case Studies and Applications
>> Industrial Scale Dehydration
>> Home Use and Small-Scale Production
● Conclusion
● FAQs
>> 1. What is the importance of cooling in food dehydration?
>> 2. How does heat pump technology benefit food dehydrators?
>> 3. What are the advantages of using dehumidification heat pumps in food dehydration?
>> 4. Why is proper ventilation important for food dehydrators?
>> 5. How can regular maintenance improve the efficiency of food dehydrators?
● Citations:
In the realm of food processing, maintaining optimal temperatures in food dehydrator machines is crucial for efficient drying and preserving nutritional value. This article delves into the strategies and technologies used to keep food dehydrator machines cool, thereby enhancing their performance and energy efficiency.

Introduction to Food Dehydrators
Food dehydrators are essential in the food industry for removing moisture from food products, which helps in preserving them for longer periods. The process involves circulating hot air around the food to evaporate its moisture content. However, managing temperature is key to preventing overheating, which can damage both the machine and the food.
Importance of Cooling in Dehydration
Cooling dense items like thick vegetable slices or fruits before dehydration can significantly reduce energy consumption. Pre-cooling these items to temperatures between 0°C and 15°C can enhance the drying process by reducing the initial moisture content, thus speeding up dehydration. This method is particularly beneficial for sensitive foods that require gentle heat treatment to preserve their nutritional value.
Technologies for Cooling Food Dehydrators
Several technologies are employed to maintain optimal temperatures in food dehydrators:
1. Heat Pump Technology
Heat pump technology is integrated into some advanced food dehydrators to manage temperature efficiently. This involves a closed-loop heat exchange system that transfers heat from the drying chamber to the external environment, ensuring consistent operating temperatures while saving energy. High-efficiency compressors and variable-speed fans are used to adjust airflow based on temperature readings, preventing overheating and reducing energy consumption by up to 75% compared to traditional methods.
2. Dehumidification Heat Pumps
Dehumidification heat pumps combine dehumidification with heat recovery, making them highly efficient for drying processes. These systems cool and dehumidify air using refrigeration while recovering moisture through the heat pump principle. This method allows for closed drying at low temperatures (7-75°C) and recycles energy during the drying process.
3. Low-Temperature Drying Machines
Some food dehydrators are designed with low-temperature drying capabilities, ensuring that the nutritional value of the food is preserved. These machines use low-pressure hot air flows and have separate drying and cooling zones to maintain stable temperatures and prevent overheating.
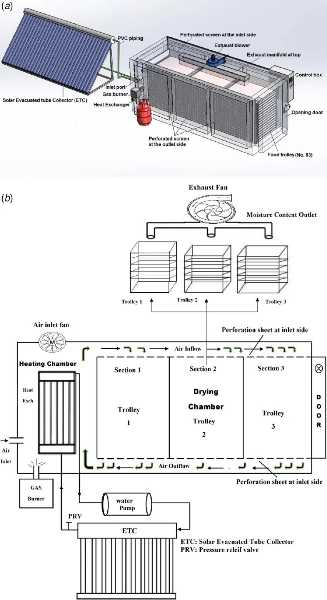
Additional Strategies for Cooling
Besides advanced technologies, there are practical strategies to keep food dehydrators cool:
1. Proper Placement and Ventilation
Placing the dehydrator in a well-ventilated area is crucial. Enclosed spaces can trap heat, causing the machine to overwork and potentially reducing its lifespan. Ensuring clearance around the machine on all sides allows for better airflow and heat dissipation.
2. Avoid Heated Areas
Positioning the dehydrator away from heated areas or direct sunlight can prevent unnecessary heat buildup. Even a slight elevation can improve airflow beneath the dehydrator, aiding in consistent temperature maintenance.
3. Regular Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance of the dehydrator can help ensure that it operates efficiently. Dust buildup can impede airflow and cause the machine to work harder, leading to increased temperatures.
4. Insulation and Thermal Management
Using thermal insulation materials around the dehydrator can help retain heat within the drying chamber while preventing external heat from affecting the machine's operation. This approach ensures that the machine operates at optimal temperatures without wasting energy.
5. Smart Sensors and Automation
Integrating smart sensors and automation systems can monitor temperature and humidity levels in real-time, adjusting the machine's operation to maintain optimal conditions. This technology ensures consistent drying quality and reduces manual intervention.
Case Studies and Applications
Industrial Scale Dehydration
In industrial settings, maintaining cool temperatures is critical for large-scale food dehydration. Companies often use centralized cooling systems that distribute chilled air throughout the facility, ensuring that all dehydrators operate within optimal temperature ranges.
Case Study:
A leading food processing company in Europe implemented a heat pump system in their dehydration facility, resulting in a 60% reduction in energy costs and a significant increase in production efficiency.
Home Use and Small-Scale Production
For home users and small-scale producers, maintaining optimal temperatures can be achieved through simpler methods such as using fans for ventilation or placing the dehydrator in a shaded area. These strategies help in reducing heat buildup and ensuring efficient operation.
Conclusion
Maintaining optimal temperatures in food dehydrators is essential for efficient drying and preserving the nutritional value of food products. By integrating advanced technologies like heat pumps and dehumidification systems, and employing practical strategies such as proper ventilation and placement, manufacturers can enhance the performance of their machines while reducing energy consumption. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more efficient solutions for cooling food dehydrator machines.
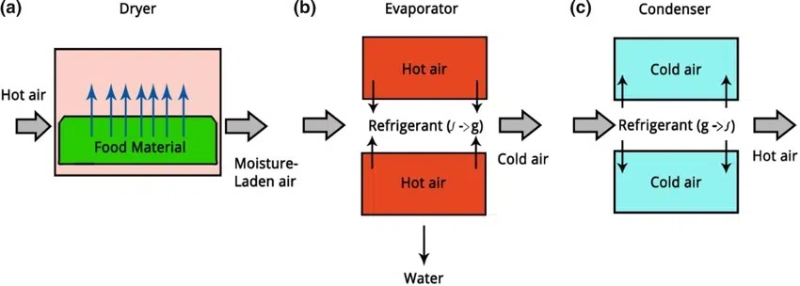
FAQs
1. What is the importance of cooling in food dehydration?
Cooling dense food items before dehydration reduces energy consumption and speeds up the drying process by lowering the initial moisture content.
2. How does heat pump technology benefit food dehydrators?
Heat pump technology helps manage temperature efficiently, prevents overheating, and saves energy by transferring heat from the drying chamber to the external environment.
3. What are the advantages of using dehumidification heat pumps in food dehydration?
Dehumidification heat pumps offer efficient drying at low temperatures, recycle energy during the process, and are not affected by external environmental conditions.
4. Why is proper ventilation important for food dehydrators?
Proper ventilation prevents heat buildup, reduces the risk of overheating, and extends the lifespan of the machine by ensuring efficient airflow.
5. How can regular maintenance improve the efficiency of food dehydrators?
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning, ensures that the machine operates efficiently by preventing dust buildup, which can impede airflow and cause overheating.
Citations:
[1] https://www.aimheatpump.com/blog-how-to-keep-the-best-food-dehydrator-machine-cold-to-speed-up
[2] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN110207480A/zh
[3] https://www.webstaurantstore.com/blog/3874/cooling-food-explained.html
[4] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN201919616U/zh
[5] https://shincci-global.com/technology/dry_food
[6] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN109252340A/zh
[7] https://www.ivins.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/RCP-Dehydrating-101.pdf
[8] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN1110593C/zh











