
Content Menu
● Understanding Food Drying
● What is a Heat Pump Dryer?
>> Benefits of Heat Pump Dryers
● What is a Condenser Dryer?
>> Benefits of Condenser Dryers
● Comparing Heat Pump Dryers and Condenser Dryers
● Applications in the Food Industry
● Choosing the Right Dryer for Your Needs
● Technological Innovations in Food Drying
● Environmental Considerations
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the main difference between heat pump dryers and condenser dryers?
>> 2. Which type of dryer is more energy-efficient?
>> 3. Can I use both types of dryers for all food products?
>> 4. Are heat pump dryers more expensive than condenser dryers?
>> 5. How do I maintain my food dryer?
In the world of food processing, drying is a crucial step that helps preserve food, enhance flavors, and prolong shelf life. With the advancement of technology, two popular types of dryers have emerged for this purpose: heat pump dryers and condenser dryers. This article will explore the differences between these two types of dryers, their benefits, and their applications in the food industry.
Understanding Food Drying
Food drying is a method used to remove moisture from food products to prevent spoilage and extend their shelf life. This process can be achieved through various methods, including air drying, sun drying, and using specialized equipment like food dryers.
Drying not only inhibits the growth of microorganisms but also helps in concentrating flavors and making food lighter and easier to transport. The choice of drying method can significantly impact the quality of the final product, making it essential for food manufacturers to select the right equipment.
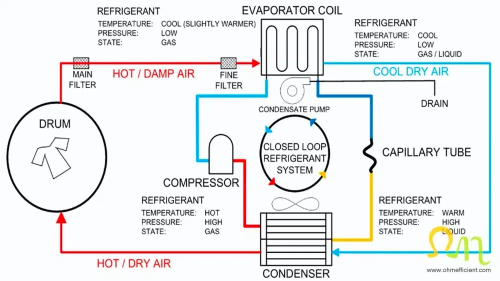
What is a Heat Pump Dryer?
A heat pump dryer is an energy-efficient appliance that uses a refrigeration cycle to dry food. It works by extracting moisture from the air inside the dryer and transferring it outside while recycling heat to maintain optimal drying temperatures.
Benefits of Heat Pump Dryers
- Energy Efficiency: Heat pump dryers use significantly less energy compared to traditional dryers, making them an environmentally friendly choice. They can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared to conventional drying methods.
- Gentle Drying: They operate at lower temperatures, which helps preserve the nutritional value and flavor of the food being dried. This is particularly important for high-value products like fruits and herbs.
- Versatility: These dryers can be used for a wide range of products, including fruits, vegetables, herbs, and meats. Their ability to adjust temperature and humidity levels allows for tailored drying processes.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: By consuming less energy, heat pump dryers contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions. This aspect is increasingly important for businesses looking to improve their sustainability practices.

What is a Condenser Dryer?
A condenser dryer, on the other hand, uses a different mechanism to dry food. It works by heating air and blowing it over the food items. The moisture from the food evaporates into the air, which is then condensed back into water and collected in a tank or drained away.
Benefits of Condenser Dryers
- Quick Drying: Condenser dryers typically operate at higher temperatures, allowing for faster drying times. This can be advantageous in commercial settings where time efficiency is critical.
- Ease of Use: They are generally straightforward to operate and require less maintenance than heat pump dryers. Most models come with automatic settings that simplify the drying process.
- Cost-Effective: While they may consume more energy than heat pump dryers, they are often less expensive upfront. This makes them an attractive option for smaller businesses or those just starting in food processing.
Comparing Heat Pump Dryers and Condenser Dryers
To help you make an informed decision about which type of dryer is best for your needs, here's a comparison table highlighting key differences:
| Feature | Heat Pump Dryer | Condenser Dryer |
| Energy Efficiency | High | Moderate |
| Drying Temperature | Low | High |
| Drying Time | Longer | Shorter |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Maintenance | More complex | Simpler |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint | Higher carbon footprint |
Applications in the Food Industry
Both heat pump dryers and condenser dryers have specific applications within the food industry:
- Heat Pump Dryers: Ideal for drying sensitive products such as fruits (e.g., apples, bananas), vegetables (e.g., tomatoes, peppers), and herbs (e.g., basil, thyme). Their gentle drying process helps retain flavor and nutrients. For instance, dried fruits produced using heat pump technology often have better color retention and taste compared to those dried with higher temperature methods.
- Condenser Dryers: Suitable for bulk drying operations where speed is essential. Commonly used for products like grains (e.g., rice, corn) and meats (e.g., jerky). The rapid drying capabilities make condenser dryers popular in large-scale operations where time constraints are critical.
Choosing the Right Dryer for Your Needs
When deciding between a heat pump dryer and a condenser dryer for your food processing needs, consider the following factors:
- Type of Food Products: If you are primarily drying delicate items that require careful handling, a heat pump dryer may be more suitable. Conversely, if you need to dry larger quantities quickly, a condenser dryer might be better.
- Energy Costs: Evaluate your energy costs and consider how much you are willing to invest in energy-efficient equipment versus initial purchase price. Over time, heat pump dryers can lead to significant savings on energy bills.
- Space Availability: Consider the physical space available for installation. Heat pump dryers may require additional space for ventilation compared to condenser models. Ensure that you have adequate room for airflow around the units to optimize their performance.
- Production Volume: Assess your production volume needs. If your operation requires continuous or high-volume drying processes, investing in multiple units or larger capacity models may be necessary.
Technological Innovations in Food Drying
Recent advancements in technology have led to improved designs and functionalities in both heat pump and condenser dryers:
- Smart Technology Integration: Many modern dryers now come equipped with smart technology that allows users to monitor and control drying processes remotely via smartphone apps. This feature enhances convenience and ensures optimal drying conditions are maintained throughout the process.
- Improved Sensors: Enhanced moisture sensors help achieve precise control over humidity levels within the dryer. This capability allows operators to adjust settings dynamically based on real-time conditions, resulting in better product quality.
- Energy Recovery Systems: Some advanced models incorporate energy recovery systems that capture waste heat from the drying process and reuse it for preheating incoming air. This innovation further boosts energy efficiency.
Environmental Considerations
As sustainability becomes increasingly important in food processing industries worldwide, choosing an environmentally friendly dryer can enhance your brand's reputation:
- Sustainable Practices: Using heat pump dryers aligns with sustainable practices due to their lower energy consumption and reduced carbon footprint. Companies adopting such technologies can market themselves as eco-friendly brands.
- Waste Reduction: Efficient drying processes minimize product waste by ensuring that more food retains its quality during processing. This aspect is crucial as businesses strive to reduce overall waste in their operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both heat pump dryers and condenser dryers have their unique advantages and applications in the food industry. The choice between them ultimately depends on your specific needs regarding efficiency, product type, drying time, budget, and environmental considerations. By understanding these differences and evaluating your requirements carefully, you can select the right dryer that meets your operational goals while ensuring high-quality dried products.

FAQ
1. What is the main difference between heat pump dryers and condenser dryers?
Heat pump dryers operate at lower temperatures using a refrigeration cycle to recycle heat and moisture efficiently. In contrast, condenser dryers use higher temperatures to evaporate moisture quickly from food items.
2. Which type of dryer is more energy-efficient?
Heat pump dryers are generally more energy-efficient due to their ability to recycle heat during the drying process.
3. Can I use both types of dryers for all food products?
While both types can be used for various products, heat pump dryers are better suited for delicate items like fruits and herbs due to their gentle drying process. Condenser dryers are ideal for bulk drying operations where speed is essential.
4. Are heat pump dryers more expensive than condenser dryers?
Yes, heat pump dryers typically have a higher initial cost but can save money in energy bills over time due to their efficiency.
5. How do I maintain my food dryer?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning filters, checking drainage systems (for condenser models), ensuring proper airflow around the unit, and periodically inspecting seals for wear or damage. Always refer to the manufacturer's guidelines for specific maintenance instructions.












