
Content Menu
● The Science of Dehydration
● Recommended Dehydrating Temperatures
● How Temperature Affects Dehydration
● Tips for Using a Food Dehydrator
● Common Uses for Dehydrated Foods
● Health Benefits of Dehydrated Foods
● Energy Efficiency of Food Dehydrators
● Creative Recipes Using a Food Dehydrator
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is the best temperature for dehydrating fruits?
>> 2. Can I dehydrate meats at lower temperatures?
>> 3. How long does it take to dehydrate vegetables?
>> 4. What happens if I set my dehydrator too high?
>> 5. Is it necessary to preheat my dehydrator?
● Citations:
Food dehydrators are essential tools for preserving fruits, vegetables, meats, and herbs by removing moisture. This process not only extends the shelf life of food but also concentrates flavors and nutrients. Understanding the optimal temperatures for dehydrating various foods is crucial for achieving the best results. In this article, we will explore the recommended temperatures for different types of food, the science behind dehydration, tips for using a food dehydrator effectively, and much more.

The Science of Dehydration
Dehydration is a method of food preservation that involves removing moisture to inhibit the growth of bacteria, yeasts, and molds. The key to successful dehydration lies in maintaining a consistent temperature and adequate airflow within the dehydrator.
- Moisture Removal: When food is heated, moisture evaporates from its surface. If the temperature is too high, the outer layer may dry too quickly, leading to a phenomenon known as "case hardening," where moisture remains trapped inside the food.
- Temperature Control: The ideal dehydrating temperature varies depending on the type of food being processed. Most fruits and vegetables dehydrate well at lower temperatures (around 125°F or 52°C), while meats require higher temperatures (around 145°F or 63°C) to ensure safety.
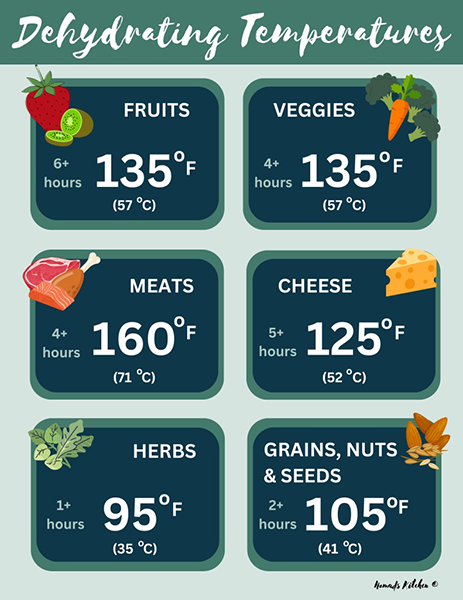
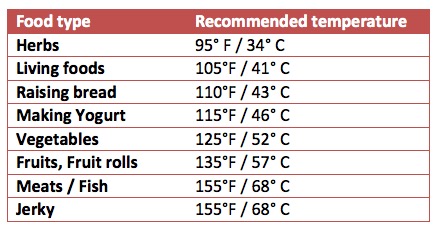
Recommended Dehydrating Temperatures
Here are some general guidelines for dehydrating various types of food:
- Fruits: 135°F (57°C) to 145°F (63°C)
- Vegetables: 125°F (51°C) to 135°F (57°C)
- Herbs: 95°F (35°C) to 115°F (46°C)
- Meats (Jerky): 155°F (68°C) to 160°F (71°C)
- Fish: 145°F (63°C)
These temperatures help preserve flavor, color, and nutritional value while ensuring that harmful microorganisms are eliminated.
How Temperature Affects Dehydration
The temperature setting on a food dehydrator can significantly impact the quality of the final product. Here's how:
- Low Temperatures: Using lower temperatures (below 118°F or 48°C) preserves enzymes and nutrients but may require longer drying times. This method is often preferred for raw foods.
- High Temperatures: Higher temperatures can speed up the drying process but may lead to nutrient loss and affect flavor. For instance, drying fruits at temperatures above 145°F can result in a loss of Vitamin C and other sensitive nutrients.
Tips for Using a Food Dehydrator
1. Preheat Your Dehydrator: Always preheat your dehydrator before adding food. This ensures that moisture starts evaporating immediately.
2. Cut Food Evenly: Slice fruits and vegetables into uniform pieces to ensure even drying. Thicker pieces will take longer to dry.
3. Avoid Overloading: Do not overcrowd trays; allow adequate space for air circulation.
4. Rotate Trays: If your dehydrator does not have a fan or automatic rotation feature, periodically rotate trays to promote even drying.
5. Check Regularly: Monitor your food as it dehydrates to prevent over-drying or under-drying.
6. Blanch Vegetables When Necessary: Some vegetables benefit from blanching before dehydration, which helps preserve color and texture while speeding up the drying process.
7. Use Proper Storage Techniques: After dehydration, store your foods in airtight containers to prevent moisture reabsorption and spoilage.
8. Condition Your Dried Foods: After drying, let your foods sit in a sealed container for a few days to equalize moisture levels before long-term storage.
Common Uses for Dehydrated Foods
Dehydrated foods are versatile and can be used in various culinary applications:
- Snacks: Dried fruits and vegetable chips make healthy snacks.
- Soups and Stews: Dehydrated vegetables can be rehydrated in soups or stews.
- Camping Food: Lightweight dehydrated meals are perfect for camping trips.
- Baking Ingredients: Dried herbs can enhance flavors in baked goods.
Health Benefits of Dehydrated Foods
Dehydrating food not only extends its shelf life but also offers several health benefits:
- Nutrient Retention: Dehydrated foods often retain more nutrients compared to those that are cooked at high temperatures.
- Fiber Content: The dehydration process increases fiber concentration in fruits and vegetables, which is beneficial for digestive health.
- Reduced Risk of Foodborne Illnesses: By removing moisture, dehydration inhibits the growth of bacteria that cause foodborne illnesses.
- Convenience and Portability: Dehydrated foods are lightweight and easy to store, making them ideal for travel or emergency preparedness.
Energy Efficiency of Food Dehydrators
Food dehydrators tend to be much more energy-efficient than conventional ovens. When comparing energy consumption:
- A typical dehydrator uses about 1000 watts over an extended period (12 hours), whereas an oven can consume between 5000 watts to over 38,000 watts during similar usage times.
This efficiency not only saves money on electricity bills but also makes dehydrators an environmentally friendly option for preserving food.
Creative Recipes Using a Food Dehydrator
Here are some creative ideas for using your food dehydrator:
1. Fruit Leather: Puree fruits such as strawberries or peaches with a bit of honey or agave syrup. Spread evenly on a fruit leather tray and dehydrate at around 135°F until pliable.
2. Vegetable Chips: Slice root vegetables like sweet potatoes or beets thinly, toss with olive oil and seasonings, then dehydrate at 135°F until crispy.
3. Herb Blends: Dry fresh herbs like basil or thyme at low temperatures (around 95°F) for use in cooking throughout the year.
4. Jerky Variations: Marinate slices of beef or turkey in your favorite sauces before dehydrating them at higher temperatures (around 155°F) for homemade jerky.
5. Granola Mixes: Combine oats with nuts, seeds, honey, and dried fruits before dehydrating into crunchy granola clusters perfect for breakfast or snacking.
Conclusion
Understanding what temperature is suitable for a food dehydrator is essential for anyone looking to preserve food effectively. By adhering to recommended temperature guidelines based on the type of food, you can ensure that your dehydrated items retain their flavor, color, and nutritional value while preventing spoilage.
In summary:
- Use lower temperatures for fruits and vegetables.
- Higher temperatures are necessary for meats.
- Always monitor your food during the dehydration process.
By following these tips and guidelines, you can maximize the benefits of your food dehydrator while enjoying delicious homemade snacks year-round.
FAQ
1. What is the best temperature for dehydrating fruits?
The best temperature for dehydrating fruits is typically between 135°F (57°C) and 145°F (63°C).
2. Can I dehydrate meats at lower temperatures?
No, meats should be dehydrated at higher temperatures (around 155°F or 68°C) to ensure safety against pathogens.
3. How long does it take to dehydrate vegetables?
Dehydrating vegetables usually takes between 6 to 12 hours depending on their thickness and moisture content.
4. What happens if I set my dehydrator too high?
Setting your dehydrator too high can lead to case hardening, where the outside dries quickly but moisture remains trapped inside.
5. Is it necessary to preheat my dehydrator?
Yes, preheating your dehydrator helps start the evaporation process immediately when you add your food.
Citations:
[1] https://www.webstaurantstore.com/guide/741/food-dehydrators-buying-guide.html
[2] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lEUA2t2XD5M
[3] https://theinspiredhome.com/articles/a-beginners-gdeletee-to-dehydrating-food/
[4] https://www.bestbuy.com/discover-learn/10-reasons-to-buy-a-food-dehydrator/pcmcat1634332391134
[5] https://www.osbheatpump.com/news/how-to-use-a-food-dehydrator-10-useful-tips-for-beginners-and-advanced-users/
[6] https://www.commercialdehydrators.com.au/dehydrating-recipes-filters
[7] https://www.webmd.com/diet/dehydrating-food-good-for-you
[8] https://www.freshoffthegrid.com/dehydrating-food/
[9] https://www.goodhousekeeping.com/appliances/a31904157/what-is-a-dehydrator/
[10] https://homesteadingfamily.com/preservation-101-intro-to-dehydrating-food/











