
Content Menu
● Introduction
● Understanding the Technology
● Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
● Drying Performance and Time
● Installation and Maintenance Requirements
● Environmental Impact and Sustainability
● Cost Considerations
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> Q1: How much more energy efficient are heat pump dryers?
>> Q2: Do heat pump dryers take longer to dry clothes?
>> Q3: Which type of dryer is better for delicate clothes?
>> Q4: What is the typical lifespan difference between the two types?
>> Q5: Are heat pump dryers worth the extra cost?
Introduction
The debate between heat pump dryers and condenser dryers has become increasingly relevant as consumers seek energy-efficient and effective laundry solutions. This comprehensive guide explores the key differences, advantages, and considerations between these two popular drying technologies, helping you make an informed decision for your home.
Understanding the Technology
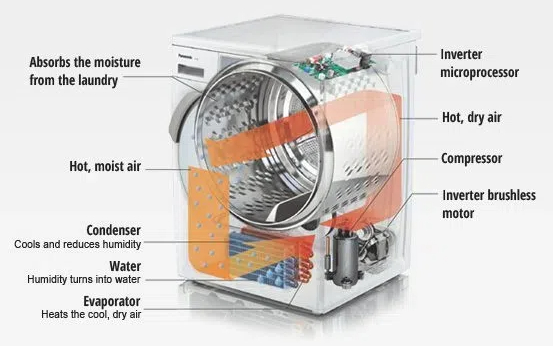
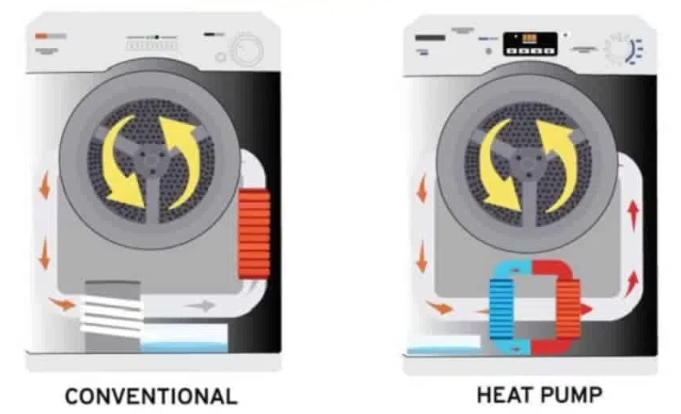
Heat pump dryers represent the latest advancement in drying technology, utilizing a sophisticated heat exchange system that recycles warm air to dry clothes efficiently. These units extract moisture from clothes using a refrigeration system similar to air conditioners, but in reverse. The process involves heating air, passing it through clothes, collecting moisture, and then reusing the heated air.
Condenser dryers, on the other hand, operate by heating air and passing it through wet clothes, then cooling the moisture-laden air to condense water into a collection tank. While simpler in design, this process requires more energy as the heated air is not recycled but rather continuously generated.

Energy Efficiency and Operating Costs
One of the most significant advantages of heat pump dryers is their superior energy efficiency. These units typically use about half the energy of conventional condenser dryers, resulting in lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact. The energy savings come from the heat pump system's ability to reuse heated air rather than continuously generating new hot air.
While the initial purchase price of heat pump dryers is generally higher, the long-term energy savings can offset this cost difference over time. For households that frequently use their dryer, the reduced energy consumption can lead to substantial savings on utility bills.
Drying Performance and Time
When it comes to drying performance, both technologies have their merits. Condenser dryers typically complete drying cycles more quickly due to their higher operating temperatures. This makes them particularly suitable for households with heavy laundry demands or those who prioritize speed over energy efficiency.
Heat pump dryers, while generally taking longer to complete a cycle, operate at lower temperatures. This gentler drying process is particularly beneficial for delicate fabrics and can help extend the lifespan of clothes by reducing wear and tear.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Both types of dryers offer flexible installation options as neither requires external venting. This makes them ideal for apartments, condominiums, or homes where venting to the outside is impractical. However, they do have different maintenance needs.
Heat pump dryers typically require less frequent maintenance, though their heat exchange system should be cleaned periodically to maintain optimal performance. Condenser dryers need regular emptying of their water collection container and cleaning of the condenser unit to prevent efficiency loss.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental benefits of heat pump dryers are significant. Their reduced energy consumption translates to a lower carbon footprint, making them an excellent choice for environmentally conscious consumers. Additionally, the lower operating temperatures and gentler drying action contribute to reduced textile waste by extending clothing lifespan.
Cost Considerations
While heat pump dryers generally command a higher purchase price, their long-term cost benefits should be considered. The energy savings can eventually offset the initial price difference, especially in households with frequent dryer usage. However, condenser dryers remain a more budget-friendly option for those with immediate cost constraints.
Conclusion
The choice between a heat pump dryer and a condenser dryer ultimately depends on individual priorities and circumstances. Heat pump dryers excel in energy efficiency, environmental impact, and gentle clothes care, making them ideal for environmentally conscious consumers who don't mind longer drying times. Condenser dryers offer faster drying times and lower upfront costs, suitable for those prioritizing speed and initial affordability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How much more energy efficient are heat pump dryers?
A: Heat pump dryers typically use about 50% less energy than conventional condenser dryers.
Q2: Do heat pump dryers take longer to dry clothes?
A: Yes, heat pump dryers generally take 30-50% longer to complete a drying cycle compared to condenser dryers.
Q3: Which type of dryer is better for delicate clothes?
A: Heat pump dryers are generally better for delicate clothes due to their lower operating temperatures and gentler drying process.
Q4: What is the typical lifespan difference between the two types?
A: Both types can last 10-15 years with proper maintenance, though heat pump dryers often have longer warranties due to their premium positioning.
Q5: Are heat pump dryers worth the extra cost?
A: For households with frequent dryer usage, heat pump dryers can be worth the extra initial cost due to long-term energy savings and gentler clothes care.












