
Content Menu
● Introduction to Drying Technologies
● Penetration Type Dryers
>> Key Features of Penetration Type Dryers:
>> Operational Principle:
>> Advantages Over Traditional Methods:
● Traditional Drying Methods
>> Direct Drying
>> Indirect Drying
>> Low-Pressure Superheated Steam Drying (LPSSD)
>> Advantages of Traditional Methods:
● Comparison of Penetration Type Dryers and Traditional Methods
● Applications of Penetration Type Dryers
>> Case Study: Drying Fruits
>> Case Study: Drying Grains
● Future Developments and Trends
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What are the primary advantages of penetration type dryers over traditional methods?
>> 2. How do penetration type dryers achieve uniform drying for stacked products?
>> 3. What types of products are best suited for penetration type dryers?
>> 4. How does the temperature control in penetration type dryers compare to traditional dryers?
>> 5. What are the operational costs of penetration type dryers compared to traditional methods?
● Citations:
In the realm of food processing, drying is a crucial step that ensures the preservation and quality of products. Among various drying technologies, penetration type dryers have emerged as a highly efficient and energy-saving option compared to traditional drying methods. This article delves into the comparison between penetration type dryers and traditional drying methods, highlighting their advantages, applications, and operational principles.

Introduction to Drying Technologies
Drying technologies are broadly categorized into direct and indirect methods, each with its own set of advantages and applications.
1. Direct Dryers: These use convection to transfer heat directly to the material being dried. Hot air or inert gases are commonly used as the heat transfer medium, which is circulated around and through the material to vaporize moisture.
2. Indirect Dryers: They use conduction to transfer heat through a partition that separates the heat transfer medium from the material. This method is ideal for sensitive items like pharmaceuticals and combustible materials.
Penetration Type Dryers
Penetration type dryers are designed to efficiently dry products that can be stacked. They utilize a patented half-vacuum air duct design, allowing hot air to penetrate through stacked products evenly. This design ensures uniform drying even when products are densely packed, making it highly suitable for large-scale industrial applications.
Key Features of Penetration Type Dryers:
1. Energy Efficiency: They use only 25% of the electricity compared to traditional dryers, making them a cost-effective option.
2. Temperature Control: Adjustable temperature settings from 18-80℃ allow for hot drying, cool drying, and dehumidification functions.
3. Capacity: Available in capacities ranging from 300 to 10 tons, catering to various industrial needs.
Operational Principle:
The operational principle involves circulating hot air through the stacked products from the bottom to the top. This ensures that all layers of the product are exposed to the drying medium, resulting in uniform moisture removal.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods:
1. Uniform Drying: Ensures consistent moisture levels across all layers of the product.
2. Energy Savings: Reduces operational costs significantly due to lower energy consumption.
3. Flexibility: Can handle a wide range of products and drying conditions.
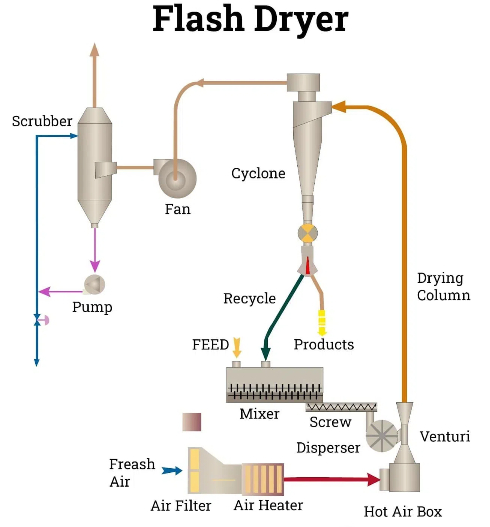
Traditional Drying Methods
Traditional drying methods include various techniques such as direct and indirect drying, as well as specialized methods like low-pressure superheated steam drying (LPSSD).
Direct Drying
Direct drying involves direct contact between the material and the drying medium (usually hot air). This method is efficient but can be energy-intensive and may require additional mechanisms to enhance heat transfer.
Indirect Drying
Indirect drying uses a conductive partition to separate the heat source from the material. It is less energy-intensive than direct drying and is suitable for sensitive materials.
Low-Pressure Superheated Steam Drying (LPSSD)
LPSSD uses superheated steam under reduced pressure to dehydrate materials. This method reduces the need for high temperatures and eliminates oxygen, making it ideal for preserving nutrients in food products.
Advantages of Traditional Methods:
1. Wide Application Range: Suitable for a variety of materials, including those requiring precise temperature control.
2. Established Technology: Well-understood and widely implemented in various industries.
3. Customization: Can be tailored to specific product requirements.
Comparison of Penetration Type Dryers and Traditional Methods
| Feature | Penetration Type Dryers | Traditional Dryers |
| Energy Efficiency | Highly efficient, using only 25% of traditional dryer energy. | Generally less efficient, especially direct dryers. |
| Temperature Control | Adjustable temperature settings for versatile drying conditions. | Often fixed temperature settings, less flexible. |
| Product Suitability | Ideal for stacked products, ensuring uniform drying. | Suitable for various products but may not ensure uniform drying for stacked items. |
| Operational Cost | Lower operational costs due to energy efficiency. | Higher operational costs, especially for direct dryers. |
Applications of Penetration Type Dryers
Penetration type dryers are particularly useful in the food industry for drying products like fruits, vegetables, and grains. Their ability to handle large volumes while maintaining energy efficiency makes them a preferred choice for industrial-scale food processing.
Case Study: Drying Fruits
In a recent application, a fruit processing company integrated penetration type dryers into their production line. The results showed a significant reduction in energy costs and improved product quality due to uniform drying.
Case Study: Drying Grains
A grain processing facility adopted penetration type dryers to dry large quantities of grains efficiently. The outcome was a substantial increase in productivity and a decrease in operational expenses.
Future Developments and Trends
As technology advances, there is a growing focus on integrating sustainable practices into drying technologies. Penetration type dryers, with their energy-efficient design, are well-positioned to meet these demands. Future developments may include further enhancements in energy efficiency and the integration of renewable energy sources.
Conclusion
Penetration type dryers offer significant advantages over traditional drying methods, particularly in terms of energy efficiency and uniform drying capabilities. As the demand for efficient and cost-effective drying solutions continues to grow, penetration type dryers are poised to play a crucial role in the food processing industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the primary advantages of penetration type dryers over traditional methods?
Penetration type dryers are more energy-efficient, using only 25% of the electricity of traditional dryers, and they ensure uniform drying even for stacked products.
2. How do penetration type dryers achieve uniform drying for stacked products?
They use a patented half-vacuum air duct design that allows hot air to penetrate through stacked products evenly, ensuring uniform moisture removal.
3. What types of products are best suited for penetration type dryers?
Penetration type dryers are ideal for products that can be stacked, such as fruits, vegetables, and grains, making them suitable for large-scale industrial food processing.
4. How does the temperature control in penetration type dryers compare to traditional dryers?
Penetration type dryers offer adjustable temperature settings from 18-80℃, allowing for hot drying, cool drying, and dehumidification functions, which is more flexible than many traditional dryers.
5. What are the operational costs of penetration type dryers compared to traditional methods?
Penetration type dryers have lower operational costs due to their high energy efficiency, making them a cost-effective option for industrial drying needs.
Citations:
[1] https://www.aimheatpump.com/products-78591
[2] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN110207480A/zh
[3] https://www.iqsdirectory.com/articles/dryer/types-of-dryers.html
[4] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN1405396A/zh
[5] https://ucanr.edu/datastoreFiles/608-208.pdf
[6] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN109252340A/zh
[7] https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7554907/
[8] https://patents.google.com/patent/CN112481977B/zh











