
Content Menu
● What Is a Food Dryer?
● Types of Food Dryers
● How Do Heat Pump Dryers Work?
● Advantages of Heat Pump Dryers
● How Do Condenser Dryers Work?
● Advantages of Condenser Dryers
● Comparison: Condensation vs Heat Pump Dryer
● Applications of Food Dryers
● Choosing the Right Food Dryer
>> Innovations in Food Drying Technology
>> Smart Technology Integration
>> Improved Insulation Materials
>> Multi-Layer Drying Trays
>> Enhanced Safety Features
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What are the main differences between condensation and heat pump dryers?
>> 2. Which dryer is better for preserving nutrients in food?
>> 3. Can I use a heat pump dryer for all types of foods?
>> 4. Are there any maintenance requirements for these dryers?
>> 5. What is the average lifespan of a food dryer?
Food drying is an essential preservation method that enhances the shelf life of various food products while retaining their nutritional value. In this article, we will explore the different types of food dryers, focusing on condensation vs heat pump dryer technologies. We will discuss their mechanisms, advantages, applications, and provide insights into choosing the right dryer for your needs.

What Is a Food Dryer?
A food dryer is a device that removes moisture from food to prevent spoilage and extend its shelf life. The drying process involves applying heat and airflow to evaporate water content from food items, resulting in dehydrated products such as fruits, vegetables, meats, and herbs.
Types of Food Dryers
1. Condenser Dryers: These dryers use a heat exchanger to cool the air and condense moisture into water, which is then collected in a tank or drained away.
2. Heat Pump Dryers: Utilizing a refrigerant cycle, heat pump dryers efficiently transfer heat from the environment to the drying chamber, allowing for lower temperature drying while maintaining energy efficiency.
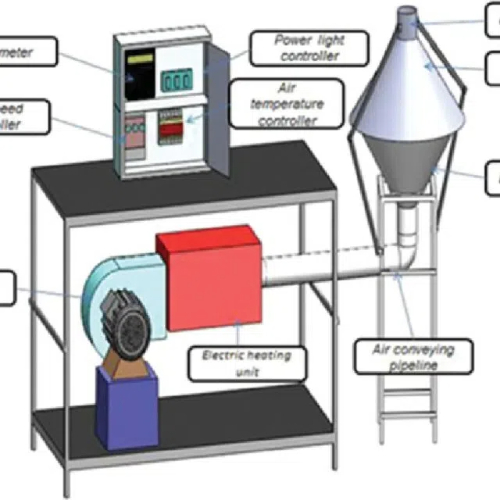
How Do Heat Pump Dryers Work?
Heat pump dryers operate by extracting moisture from food using a refrigeration cycle. Here's how they function:
1. Evaporation: The refrigerant absorbs heat from the air inside the dryer, causing it to evaporate.
2. Compression: The gas is compressed, raising its temperature.
3. Condensation: The hot gas passes through a condenser where it releases heat to the food, cooling down and turning back into a liquid.
4. Cycle Repeats: This process continues until the desired moisture level is reached in the food.
Advantages of Heat Pump Dryers
1. Energy Efficiency: Heat pump dryers consume less energy compared to traditional dryers due to their ability to recycle heat.
2. Gentle Drying: They operate at lower temperatures, which helps preserve the quality and nutritional value of food.
3. Versatility: Suitable for various types of foods including fruits, vegetables, and meats.
4. Environmentally Friendly: Lower energy consumption means reduced carbon footprint.
5. Consistent Results: Heat pump dryers provide more uniform drying results across different batches.

How Do Condenser Dryers Work?
Condenser dryers utilize a different mechanism:
1. Heating: Air is heated and circulated around the food items.
2. Moisture Collection: As moisture evaporates from the food, it cools down upon contact with a cold surface (the condenser), where it condenses back into water.
3. Water Removal: The collected water is either drained or stored in a tank for later disposal.
Advantages of Condenser Dryers
1. Ease of Use: No need for external venting; they can be placed anywhere with access to electricity.
2. Cost-Effective: Generally lower upfront costs compared to heat pump dryers.
3. Simplicity: Fewer components can mean easier repairs and maintenance.
4. Quick Setup: Ideal for users who want a straightforward solution without complex installation.
Comparison: Condensation vs Heat Pump Dryer
| Feature | Heat Pump Dryer | Condenser Dryer |
| Energy Efficiency | High (recycles heat) | Moderate (uses more energy) |
| Temperature Control | Low temperature drying | Higher temperature drying |
| Moisture Removal | Effective at low humidity | Effective but less efficient |
| Initial Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks | Easier maintenance |
Applications of Food Dryers
Food dryers are widely used in various industries:
1. Agriculture: Dehydrating fruits and vegetables for longer storage. Farmers often use these machines to preserve surplus produce during harvest seasons.
2. Food Processing: Creating snacks like jerky or dried fruits. Many companies specialize in producing healthy snacks that cater to health-conscious consumers.
3. Pharmaceuticals: Drying herbs and medicinal plants. This application is crucial for maintaining the potency and effectiveness of herbal remedies.
4. Catering Services: Chefs use dehydrated ingredients for unique dishes that require concentrated flavors or specific textures.
5. Home Use: Many households invest in food dryers for personal use to create snacks or preserve garden produce.
Choosing the Right Food Dryer
When selecting a food dryer, consider the following factors:
1. Type of Food: Different foods require different drying methods. For instance, fruits may need gentle drying at lower temperatures, while meats may require higher temperatures for safety.
2. Volume Needs: Assess how much food you plan to dry at one time. Larger operations may benefit from industrial-sized heat pump dryers, while home users might prefer smaller condenser models.
3. Energy Efficiency: Evaluate how much energy you are willing to consume versus your budget. While heat pump dryers may have higher initial costs, their long-term savings can be significant.
4. Space Considerations: Ensure you have enough space for your chosen dryer model. Some models are bulkier than others and may require additional ventilation or clearance around them.
5. Budget Constraints: Determine your budget for both initial investment and ongoing operational costs. Factor in maintenance as well.
Innovations in Food Drying Technology
Recent advancements in food drying technology have led to more efficient and user-friendly machines:
Smart Technology Integration
Many modern food dryers now come equipped with smart technology that allows users to monitor and control drying processes via mobile apps. This feature enables remote operation and alerts users when their food is ready.
Improved Insulation Materials
New insulation materials enhance energy efficiency by minimizing heat loss during the drying process. This improvement not only reduces energy consumption but also speeds up drying times.
Multi-Layer Drying Trays
Some advanced models feature multi-layer trays that allow users to dry multiple types of foods simultaneously without cross-contamination of flavors or odors.
Enhanced Safety Features
Modern dryers often include safety features such as automatic shut-off systems when doors are opened or when overheating is detected.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both condensation and heat pump dryers have their unique advantages and applications in food drying processes. Heat pump dryers offer superior energy efficiency and gentle drying capabilities, making them ideal for high-quality food preservation. On the other hand, condenser dryers are more cost-effective and easier to maintain for smaller operations.As you consider investing in a food dryer for your business or personal use, weigh these factors carefully to choose the best option that meets your needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the main differences between condensation and heat pump dryers?
Both types differ primarily in their energy efficiency and drying temperatures. Heat pump dryers recycle heat and operate at lower temperatures, while condenser dryers use higher temperatures with moderate energy efficiency.
2. Which dryer is better for preserving nutrients in food?
Heat pump dryers are better at preserving nutrients due to their lower operating temperatures compared to condenser dryers.
3. Can I use a heat pump dryer for all types of foods?
Yes, heat pump dryers are versatile and suitable for dehydrating various foods including fruits, vegetables, meats, and herbs.
4. Are there any maintenance requirements for these dryers?
Heat pump dryers require regular checks on refrigerant levels and cleaning of filters, while condenser dryers need periodic emptying of water tanks.
5. What is the average lifespan of a food dryer?
Most food dryers have an average lifespan of 10-15 years with proper maintenance.












