
Content Menu
● Introduction to Ventless Dryer Technology
● Understanding Heat Pump Clothes Dryer Efficiency
● Condenser Dryer vs. Vented Dryer: What's the Difference?
>> Vented Dryers
>> Condenser Dryers
>> Heat Pump Dryers
● Energy-Saving Laundry Appliances: The Future of Home Efficiency
● The Science Behind Moisture Removal in Ventless Dryers
● Heat Pump Dryer Pros and Cons: Is It Right for You?
>> Pros:
>> Cons:
● Compact Ventless Dryer Options for Small Spaces
● Eco-Friendly Laundry Solutions: Beyond Energy Savings
● Ventless Dryer Installation Requirements: What You Need to Know
● Heat Pump Dryer Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
● Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Laundry Technology
● Frequently Asked Questions About Ventless Heat Pump Dryers
>> 1. How long does a heat pump dryer take to dry clothes compared to a traditional dryer?
>> 2. Are heat pump dryers more expensive to repair than conventional dryers?
>> 3. Can I use dryer sheets or fabric softeners with a heat pump dryer?
>> 4. Do heat pump dryers work in cold climates?
>> 5. Can a heat pump dryer be stacked with a washing machine?
Introduction to Ventless Dryer Technology
In recent years, ventless dryer technology has gained significant popularity among homeowners and apartment dwellers alike. These innovative appliances offer a space-saving and energy-efficient alternative to traditional vented dryers. Among the various types of ventless dryers available, heat pump dryers stand out as the most advanced and eco-friendly option. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore how ventless heat pump dryers work, their benefits, and why they might be the perfect addition to your laundry room.
Understanding Heat Pump Clothes Dryer Efficiency
Heat pump clothes dryers are renowned for their exceptional energy efficiency. Unlike conventional dryers that expel hot, moist air outside, heat pump dryers recirculate and reuse the air within the appliance. This closed-loop system significantly reduces energy consumption, making them up to 50% more efficient than standard electric dryers.
The secret behind their efficiency lies in the heat pump technology itself. A heat pump dryer uses a compressor and refrigerant to heat and dehumidify the air circulating through the dryer. This process allows the dryer to operate at lower temperatures while still effectively removing moisture from your clothes.
Condenser Dryer vs. Vented Dryer: What's the Difference?
To fully appreciate the advantages of ventless heat pump dryers, it's essential to understand how they differ from traditional vented dryers and other ventless options like condenser dryers.
Vented Dryers
Vented dryers are the most common type found in many households. They work by heating air, passing it through the tumbling clothes to absorb moisture, and then expelling the hot, humid air through a vent to the outside of your home. While effective, this process can be energy-intensive and requires proper venting installation.
Condenser Dryers
Condenser dryers, another type of ventless dryer, use a heat exchanger to cool the hot, moist air from the drum, causing the water to condense. The condensed water is then collected in a reservoir or pumped directly into a drain. While more energy-efficient than vented dryers, they are not as efficient as heat pump dryers.
Heat Pump Dryers
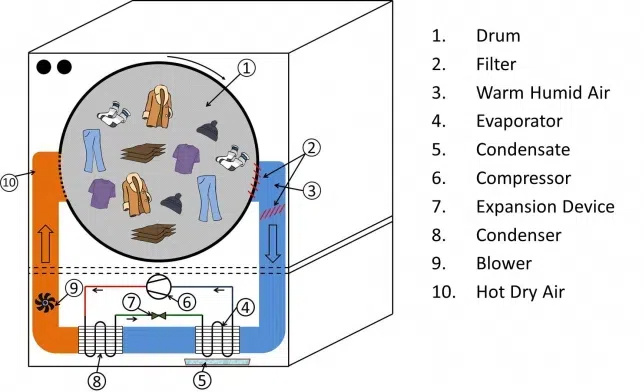
Heat pump dryers take energy efficiency to the next level. They use a heat pump to heat the air and remove moisture from clothes. The warm, moist air from the drum passes through an evaporator, which cools and condenses the water vapor. The air is then reheated by the condenser and circulated back into the drum. This closed-loop system conserves energy and allows the dryer to operate at lower temperatures, which is gentler on your clothes.
Energy-Saving Laundry Appliances: The Future of Home Efficiency
As energy costs continue to rise and environmental concerns become more pressing, energy-saving laundry appliances are becoming increasingly popular. Heat pump dryers are at the forefront of this trend, offering significant energy savings without compromising on performance.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, clothes dryers account for approximately 6% of a home's total energy use. By switching to a heat pump dryer, you can potentially cut your dryer's energy consumption in half. This not only reduces your carbon footprint but also leads to substantial savings on your energy bills over time.
The Science Behind Moisture Removal in Ventless Dryers
The process of moisture removal in ventless heat pump dryers is a fascinating example of thermodynamics in action. Let's break down the steps involved:
1. Air Circulation: The dryer begins by circulating air through the drum containing your wet clothes.
2. Evaporation: As the air passes through the clothes, it picks up moisture, becoming warm and humid.
3. Heat Exchange: The warm, moist air then passes through the evaporator coil, which is filled with cold refrigerant. This causes the moisture in the air to condense into water droplets.
4. Water Collection: The condensed water is collected in a reservoir or pumped directly into a drain.
5. Air Reheating: The now-cooler, drier air passes through the condenser coil, where it's reheated using the heat extracted during the cooling process.
6. Recirculation: The warm, dry air is then circulated back into the drum to continue the drying process.
This closed-loop system ensures that energy is conserved and reused throughout the drying cycle, maximizing efficiency.
Heat Pump Dryer Pros and Cons: Is It Right for You?
Like any appliance, heat pump dryers have their advantages and disadvantages. Let's explore them to help you decide if a heat pump dryer is the right choice for your home.
Pros:
1. Energy Efficiency: Heat pump dryers use significantly less energy than conventional dryers, leading to lower electricity bills.
2. Gentle on Clothes: The lower operating temperatures are kinder to fabrics, helping your clothes last longer.
3. No Venting Required: These dryers don't need an external vent, making them ideal for apartments or homes where venting is challenging.
4. Versatile Installation: They can be installed in various locations due to their ventless design.
5. Eco-Friendly: Lower energy consumption means a reduced carbon footprint.
Cons:
1. Higher Initial Cost: Heat pump dryers are generally more expensive to purchase than traditional dryers.
2. Longer Drying Times: The lower operating temperatures can result in longer drying cycles.
3. Capacity Limitations: Some models may have smaller capacities compared to full-sized vented dryers.
4. Maintenance: Regular cleaning of the heat exchanger and lint filter is crucial for optimal performance.
5. Ambient Temperature Sensitivity: They may be less efficient in very cold environments.
Compact Ventless Dryer Options for Small Spaces
One of the significant advantages of ventless heat pump dryers is their compact size, making them an excellent choice for small homes, apartments, or tight laundry spaces. Many manufacturers offer compact models that can fit in closets, under counters, or even stack with a washing machine to maximize vertical space.
These compact options don't sacrifice performance for size. They often come with a range of features such as multiple drying programs, delayed start options, and even smart connectivity for remote monitoring and control.
Eco-Friendly Laundry Solutions: Beyond Energy Savings
While energy efficiency is a crucial aspect of eco-friendly laundry solutions, heat pump dryers offer additional environmental benefits:
1. Water Conservation: Unlike some condenser dryers that use water for cooling, heat pump dryers don't require any water for operation.
2. Reduced Carbon Emissions: Lower energy consumption directly translates to fewer carbon emissions from power plants.
3. Longevity of Clothes: The gentler drying process helps clothes last longer, reducing textile waste.
4. No External Venting: This eliminates the loss of heated or cooled air from your home, improving overall energy efficiency.
5. Potential for Solar Integration: Their high efficiency makes heat pump dryers excellent candidates for integration with solar power systems.
Ventless Dryer Installation Requirements: What You Need to Know
Installing a ventless heat pump dryer is generally simpler than setting up a vented dryer, but there are still some important requirements to consider:
1. Electrical Requirements: Most heat pump dryers require a 240-volt electrical outlet. If you're replacing a gas dryer, you may need to install a new outlet.
2. Space Considerations: Ensure you have adequate space for the dryer, including room for the door to open fully and space for proper air circulation.
3. Drainage Options: While some models have a water collection tank, others can be connected directly to a drain. Plan for your preferred option.
4. Ambient Temperature: Heat pump dryers work best in temperatures above 50°F (10°C). If your laundry area is colder, consider heating options.
5. Ventilation: Although no external venting is required, the room should have some air circulation to prevent excessive humidity buildup.
6. Floor Stability: Ensure the floor can support the weight of the dryer, especially if you're planning to stack it with a washing machine.
Heat Pump Dryer Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
To ensure your heat pump dryer continues to operate at peak efficiency, regular maintenance is essential. Here are some key maintenance tips:
1. Clean the Lint Filter: Remove lint from the filter after every drying cycle to maintain airflow and efficiency.
2. Empty the Water Reservoir: If your model has a water collection tank, empty it regularly to prevent overflow.
3. Clean the Heat Exchanger: Follow the manufacturer's instructions to clean the heat exchanger periodically, typically every 20-30 cycles.
4. Check and Clean the Condenser: Some models have a self-cleaning condenser, but others may require manual cleaning.
5. Wipe Down the Drum: Clean the drum interior occasionally to remove any residue that might transfer to your clothes.
6. Inspect the Door Seal: Ensure the door seal is clean and intact to prevent air leaks.
7. Schedule Professional Maintenance: Consider having a professional service the dryer annually, especially if you notice any performance issues.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Laundry Technology
Ventless heat pump dryers represent a significant leap forward in laundry technology. They offer a perfect blend of energy efficiency, space-saving design, and clothes-care capabilities. While the initial investment may be higher than traditional dryers, the long-term energy savings and environmental benefits make them an attractive option for many households.
As we continue to seek ways to reduce our energy consumption and environmental impact, appliances like heat pump dryers play a crucial role in creating more sustainable homes. Whether you're renovating your laundry room, moving into a new apartment, or simply looking to upgrade your current appliances, a ventless heat pump dryer is certainly worth considering.
By understanding how these innovative dryers work and their numerous benefits, you can make an informed decision about whether a heat pump dryer is the right choice for your laundry needs. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more improvements in efficiency and performance, making the future of laundry care brighter and greener than ever before.

Frequently Asked Questions About Ventless Heat Pump Dryers
1. How long does a heat pump dryer take to dry clothes compared to a traditional dryer?
Heat pump dryers typically take about 30-50% longer to dry clothes compared to traditional vented dryers. While a conventional dryer might take about 45-50 minutes for a full load, a heat pump dryer could take 60-75 minutes. However, this longer drying time is offset by the significant energy savings and gentler treatment of fabrics.
2. Are heat pump dryers more expensive to repair than conventional dryers?
Heat pump dryers can be more expensive to repair due to their more complex technology. However, they often have longer lifespans than conventional dryers, which can offset the potential repair costs over time. Regular maintenance can help prevent many issues and extend the life of the appliance.
3. Can I use dryer sheets or fabric softeners with a heat pump dryer?
It's generally not recommended to use dryer sheets or liquid fabric softeners with heat pump dryers. These products can leave residues that clog filters and reduce efficiency. Instead, consider using wool dryer balls or adding fabric softener during the wash cycle if desired.
4. Do heat pump dryers work in cold climates?
Heat pump dryers can work in cold climates, but their efficiency may be slightly reduced in very cold environments. For optimal performance, it's best to install the dryer in a space that maintains a temperature above 50°F (10°C). In colder areas, consider heating your laundry space or choosing a model specifically designed for colder climates.
5. Can a heat pump dryer be stacked with a washing machine?
Many heat pump dryer models are designed to be stackable with compatible washing machines. This can be an excellent space-saving solution for small laundry rooms or apartments. However, always check the manufacturer's specifications and use the appropriate stacking kit to ensure safe installation.












