
Content Menu
● Introduction
● Understanding Heat Pump Dryers
>> How Heat Pump Dryers Work
● Benefits of Heat Pump Dryers for Food Products
>> Applications in Food Industry
>> Detailed Mechanism of Heat Exchange
● Comparison with Traditional Drying Methods
● Economic Considerations
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What are the main advantages of using a heat pump dryer for food?
>> 2. How does a heat pump dryer differ from traditional dryers?
>> 3. Can heat pump dryers be used for all types of food?
>> 4. What maintenance do heat pump dryers require?
>> 5. Are there any downsides to using heat pump dryers?
Introduction
Heat pump dryers have revolutionized the way we dry food products, offering a highly efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional drying methods. This article will delve into how heat pump dryers work, particularly focusing on their heat exchange process, and explore their applications in food drying. We will also highlight the benefits of using heat pump technology in the food industry, providing insights into its operational mechanics and advantages over conventional drying methods.
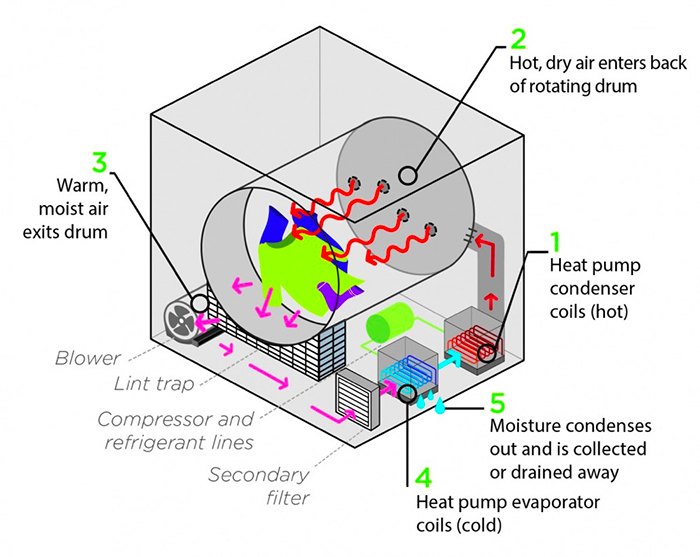
Understanding Heat Pump Dryers
A heat pump dryer operates on the principle of transferring heat from one place to another. Unlike conventional dryers that expel hot air after use, heat pump dryers recycle the air, making them more energy-efficient. The core components of a heat pump dryer include:
- Compressor: Increases the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant.
- Evaporator: Absorbs heat from the environment and evaporates the refrigerant.
- Condenser: Releases heat into the drying chamber while condensing the refrigerant back into a liquid.
- Expansion Valve: Reduces the pressure of the refrigerant, allowing it to evaporate again.
How Heat Pump Dryers Work
1. Air Circulation: The dryer draws in ambient air, which is then heated by passing through the compressor. This heated air is circulated through the drying chamber containing the food products.
2. Moisture Absorption: As the warm air circulates around the food, it absorbs moisture. The moisture-laden air is then directed to the evaporator.
3. Heat Exchange Process:
- In the evaporator, the moisture from the air is condensed into liquid water, while the air itself cools down.
- The refrigerant absorbs this heat, evaporating into a gas as it moves to the compressor.
- The compressor then compresses this gas, raising its temperature and pressure before sending it back to the condenser.
4. Reheating and Recirculation: The cooled air is reheated in the condenser and sent back into the drying chamber to continue absorbing moisture from the food until it is adequately dried.
5. Condensation and Collection: The condensed moisture is collected in a reservoir or drained away, depending on the system design.
Benefits of Heat Pump Dryers for Food Products
Using heat pump dryers for food processing offers numerous advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: By recycling hot air, these dryers consume significantly less energy compared to traditional methods that constantly generate new hot air.
- Gentle Drying: The ability to control temperatures allows for gentle drying processes that preserve nutrients and flavors better than conventional high-temperature drying methods.
- Quality Preservation: Products dried with heat pump technology retain their color, aroma, and nutritional value more effectively due to lower drying temperatures.
- Versatility: Heat pump dryers can be used for a wide range of food products including fruits, vegetables, meats, and herbs.
Applications in Food Industry
Heat pump technology is increasingly being adopted in various sectors of the food industry:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Ideal for drying sensitive produce without compromising quality. For example, apples can be dried at lower temperatures to maintain their crispness and flavor.
- Meat Products: Effective for dehydrating meats while maintaining safety standards. This process can help create jerky or dried meat snacks that are both tasty and safe for consumption.
- Herbs and Spices: Preserves essential oils and flavors during processing. Dried herbs retain their aromatic properties better when dried using low-temperature methods typical of heat pump dryers.
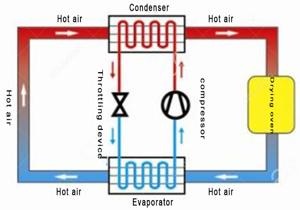
Detailed Mechanism of Heat Exchange
The heart of a heat pump dryer lies in its heat exchange mechanism. Understanding this process is crucial for appreciating how these machines achieve such high efficiency levels:
1. Refrigerant Cycle:
- The refrigerant used in heat pump dryers is vital for transferring heat throughout the system. It changes states from liquid to gas and back again as it absorbs and releases heat.
- When heated gas enters the condenser, it releases its thermal energy into the drying chamber while cooling down and turning back into a liquid state.
2. Heat Transfer Efficiency:
- The efficiency of heat transfer in a heat pump dryer is significantly higher than in traditional dryers because it utilizes both latent (moisture removal) and sensible (temperature increase) heat.
- This dual mechanism allows for faster drying times while using less energy overall.
3. Temperature Control:
- One of the standout features of heat pump dryers is their ability to maintain precise temperature controls throughout the drying process.
- This capability not only ensures consistent product quality but also prevents overheating, which can damage sensitive food items.
Comparison with Traditional Drying Methods
To fully appreciate how heat pump dryers stand out in food processing, it's essential to compare them with traditional drying methods:
| Feature | Heat Pump Dryer | Traditional Dryer |
|------------------------|--------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|
| Energy Consumption | Low (recycles hot air) | High (generates new hot air constantly) |
| Temperature Control | Precise control | Often lacks precise control |
| Product Quality | High retention of nutrients/flavors | Higher risk of nutrient loss |
| Versatility | Suitable for various foods | Limited by specific food types |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint | Higher emissions |
Economic Considerations
While initial costs for purchasing a heat pump dryer may be higher than traditional systems, several factors contribute to long-term savings:
- Reduced Energy Costs: Due to their energy-efficient design, businesses can save significantly on electricity bills over time.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Heat pump systems generally require less maintenance than traditional dryers since they operate at lower temperatures and have fewer moving parts exposed to wear.
- Extended Product Shelf Life: By preserving quality better than conventional methods, products dried with heat pumps can command higher prices in markets focused on quality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat pump dryers represent a significant advancement in food processing technology. Their ability to recycle heat not only enhances energy efficiency but also improves product quality by allowing for lower temperature drying processes. As industries continue to seek sustainable practices, heat pump dryers are poised to play an essential role in modern food processing operations.
By understanding how these systems operate—particularly their innovative heat exchange processes—manufacturers can make informed decisions about adopting this technology for improved efficiency and product quality.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the main advantages of using a heat pump dryer for food?
Heat pump dryers are energy-efficient, preserve product quality better than conventional methods, allow for precise temperature control, and can handle a variety of food products effectively.
2. How does a heat pump dryer differ from traditional dryers?
Unlike traditional dryers that expel hot air after use, heat pump dryers recycle warm air by condensing moisture and reheating it for continuous use within the drying chamber.
3. Can heat pump dryers be used for all types of food?
Yes, they are versatile enough to dry fruits, vegetables, meats, herbs, and even some dairy products without compromising quality.
4. What maintenance do heat pump dryers require?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning filters, checking refrigerant levels, ensuring that condensate drains are clear to maintain optimal performance.
5. Are there any downsides to using heat pump dryers?
While they are more energy-efficient and effective at preserving quality, initial investment costs can be higher than traditional drying systems; however, operational savings often offset this over time.
By understanding how heat pump dryers work and their benefits in food processing, manufacturers can make informed decisions about adopting this technology for improved efficiency and product quality.












