Content Menu
● Understanding Heat Pump Dryers
● How Much Heat Does A Heat Pump Dryer Give Off?
● Advantages of Using Heat Pump Dryers for Food Drying
● Components of a Heat Pump Dryer
● Operating Principles
● Applications of Heat Pump Dryers
● Efficiency Metrics
● Factors Influencing Heat Output
● Maintenance Considerations
● Conclusion
● FAQ
>> 1. What is a heat pump dryer?
>> 2. How does a heat pump dryer differ from conventional dryers?
>> 3. Can I use a heat pump dryer for all types of food?
>> 4. What are the benefits of using a heat pump dryer?
>> 5. How long does it take to dry food using a heat pump dryer?
● Citations:
Heat pump dryers are becoming increasingly popular in both residential and industrial settings due to their energy efficiency and effectiveness in drying various materials. In this article, we will explore the workings of heat pump dryers, particularly focusing on food drying applications, their benefits, and the amount of heat they generate during operation.

Understanding Heat Pump Dryers
Heat pump dryers operate on a unique principle that differentiates them from traditional dryers. They use a closed-loop system to transfer heat from the environment into the drying chamber. This process involves:
- Heat Absorption: The dryer absorbs low-temperature heat from the air.
- Heat Compression: This heat is then compressed, which increases its temperature.
- Heat Distribution: The high-temperature air is circulated within the drying chamber to remove moisture from the food or other materials.
- Moisture Removal: The humid air is expelled outside after passing through a dehumidifier.
This cycle allows heat pump dryers to operate at lower temperatures compared to conventional dryers, making them gentler on sensitive materials such as food.
How Much Heat Does A Heat Pump Dryer Give Off?
The amount of heat produced by a heat pump dryer during operation can vary based on several factors, including:
- Type of Material Being Dried: Different foods or materials require varying amounts of heat for effective drying. For instance, fruits and vegetables generally need less heat compared to meats.
- Drying Conditions: The temperature and humidity levels set within the dryer also influence the amount of heat generated. Typically, food drying occurs at temperatures ranging from 20°C to 80°C (68°F to 176°F).
- Drying Time: The duration of the drying cycle affects how much heat is utilized. Longer cycles may result in more cumulative heat output.
On average, a heat pump dryer can produce around 1.5 to 2 times more energy in the form of heat than it consumes in electricity due to its efficient energy recovery system. This means that for every kilowatt-hour (kWh) consumed, it can generate approximately 2 kWh of heat energy.
Advantages of Using Heat Pump Dryers for Food Drying
Using heat pump dryers for food processing offers numerous benefits:
- Energy Efficiency: Heat pump dryers consume significantly less energy compared to traditional drying methods. They can reduce energy use by at least 28% compared to standard dryers.
- Nutrient Preservation: By operating at lower temperatures, these dryers help retain the nutritional value of food, preserving vitamins and minerals that might otherwise be lost in higher-temperature drying processes.
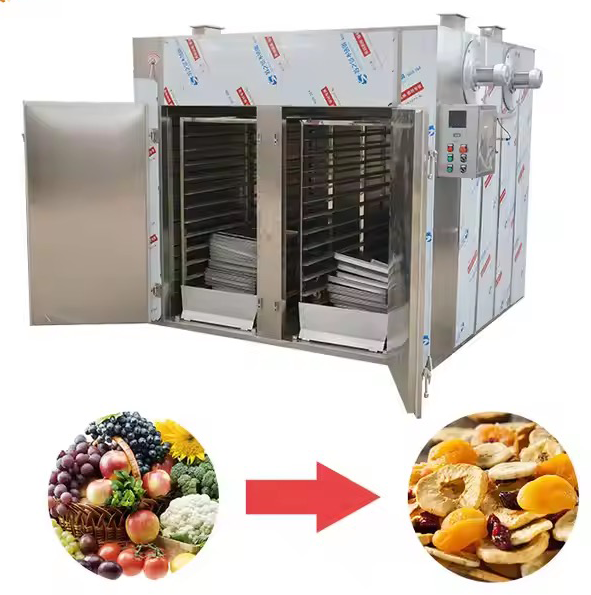
- Versatility: Heat pump dryers can accommodate a wide variety of materials including fruits, vegetables, meats, herbs, and even seafood. This versatility makes them suitable for various industries.
- Environmentally Friendly: These dryers are more sustainable as they minimize energy consumption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with traditional drying methods.
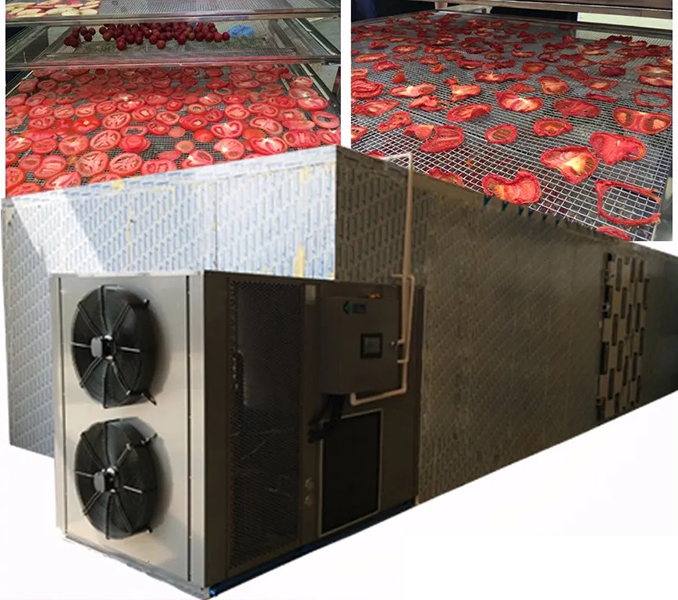
Components of a Heat Pump Dryer
A typical heat pump dryer consists of several key components:
- Heat Pump Unit: This is the core component that absorbs and compresses air.
- Drying Chamber: Where the actual drying takes place; it is insulated to maintain temperature.
- Fan System: Circulates hot air throughout the chamber for even drying.
- Control System: Allows users to set specific temperatures and humidity levels based on the material being dried.

Operating Principles
The operation of a heat pump dryer can be broken down into several steps:
1. Air Intake: Ambient air is drawn into the dryer.
2. Heat Exchange: The air passes over evaporator coils where it absorbs moisture and low-grade heat.
3. Compression: The refrigerant in the system is compressed, raising its temperature significantly.
4. Heating Air: The hot refrigerant then heats up the air that will be circulated in the drying chamber.
5. Drying Process: The heated air enters the drying chamber where it removes moisture from the food items placed inside.
6. Dehumidification: The now humid air exits through a dehumidifier before being expelled outside or recirculated back into the system.
Applications of Heat Pump Dryers
Heat pump dryers are widely used across various sectors including:
- Food Industry: For dehydrating fruits, vegetables, meats, and herbs.
- Agriculture: Drying grains and seeds.
- Pharmaceuticals: Drying medicinal herbs and compounds.
- Construction Materials: Drying wood products and other building materials.
Efficiency Metrics
To further understand how much heat a heat pump dryer gives off during operation, it's essential to consider efficiency metrics such as Coefficient of Performance (COP). The COP measures how effectively a dryer converts electrical energy into useful heating energy. For most modern heat pump dryers:
COP = Output Heat Energy / Input Electrical Energy
A higher COP indicates better efficiency; many models achieve COP values between 3 and 5, meaning they produce three to five times more thermal energy than they consume in electrical energy.
Factors Influencing Heat Output
Several factors can influence how much heat is generated during operation:
- Ambient Temperature: Higher ambient temperatures can improve efficiency as there is more available warmth for absorption.
- Humidity Levels: High humidity can increase energy consumption because more energy is needed to extract moisture from the air.
- Load Size: Overloading or underloading the dryer can affect performance; optimal load sizes ensure efficient airflow and heating.
Maintenance Considerations
To ensure optimal performance and efficiency from your heat pump dryer, regular maintenance is crucial:
- Cleaning Filters: Clogged filters can restrict airflow and reduce efficiency.
- Checking Seals: Ensure that door seals are intact to prevent warm air from escaping.
- Periodic Inspections: Regular checks on components like fans and compressors will help identify issues before they lead to significant problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat pump dryers represent an innovative solution for efficient food drying while minimizing energy consumption. They not only provide significant savings on operational costs but also enhance product quality by preserving nutrients and flavors during the drying process. Understanding how much heat these dryers generate during operation helps manufacturers optimize their processes for better efficiency and output. With their versatility across various industries—from food production to pharmaceuticals—heat pump dryers are poised to play a crucial role in sustainable manufacturing practices moving forward.

FAQ
1. What is a heat pump dryer?
A heat pump dryer is an appliance that uses a closed-loop system to absorb ambient heat and use it for drying materials efficiently without losing significant energy.
2. How does a heat pump dryer differ from conventional dryers?
Unlike conventional dryers that vent hot air outside, heat pump dryers recycle air within the system, making them more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
3. Can I use a heat pump dryer for all types of food?
Yes, heat pump dryers can effectively dry a wide range of foods including fruits, vegetables, meats, herbs, and seafood due to their adjustable temperature settings.
4. What are the benefits of using a heat pump dryer?
Benefits include energy efficiency, preservation of nutrients in food, versatility for different materials, and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional drying methods.
5. How long does it take to dry food using a heat pump dryer?
Drying times vary depending on the type of food and moisture content but typically range from 4 to 8 hours for most items when set at appropriate temperatures.
Citations:
[1] https://www.bxdrymachine.com/food-drying-machine.html
[2] https://www.webstaurantstore.com/guide/741/food-dehydrators-buying-guide.html
[3] https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/industrial-food-dryer-ultimate-guide-jack-wu-zch2c
[4] https://www.energystar.gov/products/clothes_dryers/heat-pump-dryer
[5] https://www.greenbuildingadvisor.com/article/heat-pump-clothes-dryers
[6] https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/food-dehydrator.html
[7] https://www.ike.cn/video.html
[8] https://www.fisherpaykel.com/nz/laundry/dryers/heat-pump/9kg-series-9-heat-pump-dryer-steam-care-dh9060fsg1-93294.html
[9] https://industrialdryers.com/food-dryers/
[10] https://etsolutions.in/10-amazing-benefits-of-electrical-food-dehydrator-machines/
[11] https://www.choice.com.au/home-and-living/laundry-and-cleaning/dryers/articles/what-is-a-heat-pump-dryer
[12] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fP2rSLjys4











