
Content Menu
● Understanding the Types of Dryers
>> Heat Pump Dryers
>> Condenser Dryers
>> Vented Dryers
● Comparison of Dryer Types
● Choosing the Right Dryer for Your Needs
● Applications in Food Processing
>> Heat Pump Dryers in Food Processing
>> Condenser Dryers for Packaged Foods
>> Vented Dryers for Bulk Operations
● Environmental Considerations
● Cost Analysis Over Time
>> Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Savings
>> Maintenance Costs
● Conclusion
● Frequently Asked Questions
>> 1. What is the main advantage of heat pump dryers?
>> 2. How often do I need to empty the water tank in a condenser dryer?
>> 3. Can I install a vented dryer anywhere?
>> 4. Are heat pump dryers worth the investment?
>> 5. What type of dryer is best for delicate fabrics?
When it comes to drying clothes, choosing the right dryer can make a significant difference in efficiency, cost, and convenience. For those in the food industry or involved in food processing, understanding the nuances of different drying technologies is equally important. This article will explore the three main types of dryers—heat pump, condenser, and vented—highlighting their features, benefits, and best applications.
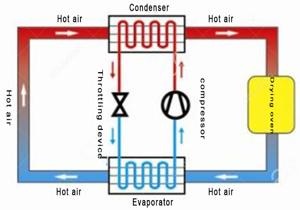
Understanding the Types of Dryers
Heat Pump Dryers
Heat pump dryers are known for their energy efficiency and gentle drying capabilities. They operate by using a closed-loop system that recycles hot air generated during the drying process. This means that instead of expelling hot air outside, heat pump dryers reheat and reuse it to continue drying clothes.
- Energy Efficiency: Heat pump dryers are the most energy-efficient option available. They consume significantly less electricity compared to other types of dryers because they operate at lower temperatures.
- Gentle on Fabrics: The lower drying temperatures are ideal for delicate fabrics, reducing wear and tear on clothing.
- Cost: While the initial purchase price is higher than that of vented or condenser dryers, the long-term savings on energy bills can offset this cost.
- Installation Flexibility: These dryers do not require external venting, allowing for more flexible installation options within a home or facility.
Condenser Dryers
Condenser dryers collect moisture from clothes and convert it into water, which is then stored in a removable tank or drained away through plumbing.
- Convenience: They can be placed anywhere with adequate ventilation since they do not need an external vent. This makes them suitable for apartments or spaces without access to outdoor vents.
- Moderate Energy Use: While more efficient than vented dryers, condenser dryers still consume more energy than heat pump models.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance is required to empty the water tank and clean the filters to ensure optimal performance.
Vented Dryers
Vented dryers work by expelling moist air outside through a vent. This type of dryer is often favored for its simplicity and speed.
- Quick Drying Times: Vented dryers typically have faster drying times compared to both heat pump and condenser models due to their ability to expel moisture directly outside.
- Lower Purchase Cost: They are generally less expensive to purchase than heat pump or condenser dryers.
- Energy Consumption: However, they are less energy-efficient and can lead to higher utility bills over time.
- Installation Requirements: Vented dryers need to be installed near an external wall or window where the vent can be connected, limiting placement options.

Comparison of Dryer Types
To help you make an informed decision, here's a comparison table highlighting key features of each dryer type:
| Feature | Heat Pump Dryer | Condenser Dryer | Vented Dryer |
| Energy Efficiency | Highest | Moderate | Lowest |
| Drying Time | Slowest | Medium | Fastest |
| Operating Temperature | Low (50°C) | High (70-75°C) | High (70-75°C) |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular (water tank) | Low |
| Installation Flexibility | High | High | Low |
Choosing the Right Dryer for Your Needs
When selecting a dryer, consider your specific needs and circumstances:
- For Energy Efficiency: If minimizing energy costs is your priority, a heat pump dryer is your best bet. It's especially suitable for businesses focused on sustainability or those looking to reduce operational costs over time.
- For Quick Drying Needs: If you require rapid drying—perhaps due to high turnover in laundry loads—a vented dryer may be more appropriate despite its higher energy consumption.
- For Versatility in Placement: If space is limited or you cannot install a venting system, a condenser dryer offers flexibility without sacrificing performance.
Applications in Food Processing
In food processing and preservation industries, the choice of dryer can significantly impact product quality and operational efficiency:
Heat Pump Dryers in Food Processing
These are particularly beneficial for drying fruits and vegetables as they preserve nutrients better due to lower temperatures. Additionally, heat pump technology allows for precise control over humidity levels during the drying process, which is crucial for maintaining the quality of sensitive food products.
Condenser Dryers for Packaged Foods
Ideal for drying packaged foods where moisture control is critical before packaging. Their ability to collect moisture internally minimizes contamination risks. This feature is especially important in maintaining food safety standards in commercial kitchens and food production facilities.
Vented Dryers for Bulk Operations
In scenarios where large quantities need quick turnaround times—such as in commercial kitchens—vented dryers can handle high volumes efficiently. Their speed makes them suitable for operations that require immediate access to clean linens or uniforms.
Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of each dryer type cannot be overlooked. As businesses become more conscious of their carbon footprint, selecting an energy-efficient dryer becomes increasingly important:
- Heat Pump Dryers: These dryers have a lower environmental impact due to their high energy efficiency. By using less electricity, they contribute to reduced greenhouse gas emissions over time.
- Condenser Dryers: While not as efficient as heat pump models, they still offer some environmental benefits by eliminating the need for external venting systems that can contribute to heat loss in buildings.
- Vented Dryers: These tend to have the highest environmental impact due to their energy consumption and reliance on external ventilation systems. Businesses using these dryers should consider their overall energy usage when evaluating sustainability practices.
Cost Analysis Over Time
Understanding the total cost of ownership is crucial when selecting a dryer type:
Initial Costs vs. Long-Term Savings
While heat pump dryers may have higher upfront costs—often ranging from 20% to 50% more than vented models—their energy savings can lead to significant cost reductions over time. For example:
- A typical heat pump dryer might save an average household approximately $100 annually on electricity bills compared to a vented dryer.
- Over five years, this could amount to $500 in savings, making the initial investment worthwhile for many users.
Maintenance Costs
Maintenance costs also vary between dryer types:
- Heat pump dryers generally require less frequent maintenance due to their closed-loop systems.
- Condenser dryers necessitate regular cleaning of filters and emptying water tanks.
- Vented dryers may require occasional duct cleaning to ensure optimal airflow but typically have lower maintenance needs overall.
Conclusion
Choosing between heat pump, condenser, and vented dryers depends on various factors including energy efficiency, cost considerations, space availability, and specific application needs. For food processing operations seeking long-term savings and quality preservation, heat pump dryers emerge as the most advantageous option despite their higher upfront costs. Conversely, for those prioritizing speed and lower initial investment without concerns about energy consumption, vented dryers may be preferable.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the main advantage of heat pump dryers?
- Heat pump dryers are highly energy-efficient and gentle on fabrics due to their low operating temperatures.
2. How often do I need to empty the water tank in a condenser dryer?
- You should empty the water tank after each use or when prompted by the machine's indicator light.
3. Can I install a vented dryer anywhere?
- No, vented dryers require installation near an external wall or window for proper ventilation.
4. Are heat pump dryers worth the investment?
- Yes, despite their higher initial cost, they offer significant savings on energy bills over time.
5. What type of dryer is best for delicate fabrics?
- Heat pump dryers are best for delicate fabrics as they operate at lower temperatures that prevent damage.












